It is mind-blowing and fascinating how every part of our daily lives is being affected by machine learning driven applications and most of us go by our mundane life routines oblivious to this. Yet, to the average non-computer science or tech guys, at the mention of machine learning and deep learning in a conversation, they totally zoom out to this seemingly esoteric concept.
The primary objective of this article is to provide a simple explanation to the question of what machine learning is in such a way that readers including those from a non-computer science background can have a basic understanding and hopefully pique an interest in the field. Towards the end of this article I have highlighted some day-to-day applications you and I use without any clue they are powered by machine learning algorithms. You will be surprised as I was when I delved into this futuristic field, so make sure you keep reading to the end.
Now lets go back to the question of the day!!
What is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning is a branch of artificial intelligence that provides computer systems the ability to automatically learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed.
Just as the name machine learning suggest:
Machine Learning implies Machine learns!!
Oh Beltus wait a second!!. But how on earth does it do that??
Hold on guys, one step at a time. Just keep reading, we are getting there soon
Machine Learning Methods.
Basically Machine learning can be categorized into supervised and unsupervised learning.
1 . Supervised Machine Learning.

Supervised machine learning involves the training of computer system using data that is explicitly Labeled. Labeled data here means that the input and desired output (target) is known. The machine learning algorithm (model) learns from this labeled data through an iterative process which then enables it to perform future predictions.
It is called supervised learning because the process of an algorithm learning from the training dataset can be thought of as a teacher supervising the learning process (student). Initially during training, we know the correct answers, the algorithm iteratively makes predictions on the training data and is corrected by the teacher. Learning stops when the algorithm achieves an acceptable level of performance. Supervised learning problems can be further grouped into regression and classification problems.
Since this is an introduction to machine learning, I have tried to keep the explanation as simple and short as possible. However, I have dedicated a separate article to Supervised machine learning
2. Unsupervised Machine Learning Algorithms
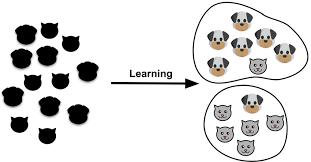
I came up with this analogy to help you better understand unsupervised learning.
Think of unsupervised learning algorithm like a completely blind person that has been asked to plunge his hand into a bowl containing different types of fruits and separate these fruits into their different groups. Key point to note here is that he has no idea about the fruits. Maybe he will group them based on shape, size or whatever I don’t know.
Here, imagine the blind person is the learning algorithm (model) and the fruits are the input data. Whatever the results(outcome) the blind man brings forth at the end of the exercise (training) is left unto you the data scientist to figure out if it makes any sense to you or not. This is exactly what unsupervised learning algorithms under the hood.
It is worth emphasizing on that the major difference between Supervised and Unsupervised learning algorithms is the absence of data labels in the latter. In unsupervised learning, the learning algorithm or model is given data with no labels or targets. It’s objective is to infer patterns in the data during training and make decisions on how to label or group them (usually with numbers 0,1,2..) based on some particular unsupervised learning algorithm. In this article, I have provided more information on unsupervised learning in a fun and easy to understand format.
Too much of information to grasp. Believe me, I know. So here is a fun fact to massage your brain.
Elephants are the only animals on earth that can die of a heartbreak when they loose a mate. How sad and ironical. The bigger the emotionally weaker. Poor Elephants…
Enough about Elephants. If you are still with me, then, let’s get back to some applications of machine learning in our daily lives.
Daily-Life Applications of Machine Learning Algorithms .
I am confident most of you are oblivious of how your day-to-day lives are being affected by machine learning driven applications. So let me shine some light on the most common applications whose backbone is machine learning.
1. Google Maps
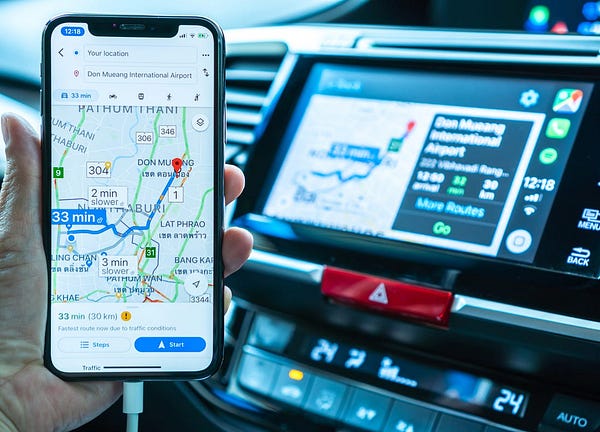
Oh the amazing google maps is the first application that comes to mind. Google Map uses Machine Learning and Big Data couple for traffic estimation.
2. FaceBook Face Recognition
Yes facebook too!. Facebook uses machine learning for automatic friend tagging and friend suggestions. So now you know why “Estella” was suggested to you as a friend by facebook.
3. Online Video Streaming.

If you are a fan of Netflix then you should know Netflix algorithms constantly gathers massive amounts of data about your various activities such as pause, rewind, or fast forward, the day you watch shows/movies (, date and time you watch, ratings and searches, browsing /scrolling behaviour and a lot more and by using their Recommender system, and powerful machine learning algorithms they are able to keep you glued to your screens.
4. Google translate.
Can’t count the number of times google translate saved my life in Istanbul. It uses Natural Language Processing Techniques to improve translation between text
5. Others applications
The list of machine learning applications is endless. So here are some other common applications that include medical diagnosis, self-driving cars, handwriting to text conversion, speech recognition, image compression, robotics, fraud detection among many others.
Hopefully, you enjoyed reading this article as much I did enjoy writing it. Suggestions and comments are highly appreciated.

Leave a comment